Methods for predicting the sensitivity of a subject suffering of renal cancer to cancer treatment
Référence
08504-01
Statut des brevets
European priority patent application n° 16305411.7 filed on April 08, 2016 and entitled “METHODS AND KITS FOR PREDICTING THE SENSITIVITY OF A SUBJECT SUFFERING OF RENAL CANCER TO CANCER TREATMENT”
Inventeurs
Gilles PAGES
Statut commercial
Exclusive or non-exclusive license
Collaborative agremment
Laboratoire
Institut de recherche sur le cancer et le vieillissement (IRCAN), UMR7284, Nice, FRANCE
Description
CONTEXT
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a renal cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, the very small tubes in the kidney that filter the blood and remove waste products. Clear cell metastatic renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 80% of cases. It is also known to be the most lethal of all the genitourinary tumors.
Although existing treatments (targeted therapies such as sunitinib, temsirolimus, bevacizumab, interferon-alpha, and sorafenib; anti-angiogenic therapies…) have improved the clinical outcome of metastatic ccRCC, heterogeneity of the patient’s response imposes new efforts to identify the best regimen according to patient profile. The present technology aims to improve the future management of these patients by means of predictive biomarkers.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The present invention relates to a method of predicting or monitoring the sensitivity of a subject having a tumor to cancer treatment (also herein identified as “chemotherapy”), in particular a method of predicting or monitoring the sensitivity of a subject having renal cell carcinoma (RCC) to an inhibitor of a tyrosine kinase receptors or an antibody selected from nivolumab, atezolizumab and avelumab, to a method of selecting an appropriate treatment of cancer, to a method of screening or identifying a compound suitable for improving the treatment of a cancer, and to corresponding kits. The method of predicting or monitoring the sensitivity of a subject having renal cell carcinoma (RCC) to an inhibitor of a tyrosine kinase receptor or to an antibody selected from nivolumab, atezolizumab and avelumab typically comprises:
- a step of determining, in a biological sample from said subject, the expression level of at least CXCL5 or CXCL7*, preferably of CXCL5 and CXCL7, and when the expression level(s) is(are) determined,
- a step of comparing said expression level(s) to a reference expression level, thereby assessing or monitoring whether the subject having ccRCC is responsive or resistant to the inhibitor of a tyrosine kinase receptor or antibody.
* (CXCL5) : CXC chemokine family that is also known as epithelial-derived neutrophil-activating peptide 78 (ENA-78)
(CXCL7) : CXC chemokine family that is also known as Neutrophil Activating Peptide-2, NAP-2
DEVELOPMENT STAGE
In metastatic ccRCC cancer, the candidate chemotherapeutic drug being an inhibitor of a tyrosine kinase receptor, in particular sunitinib, the CXCR5 reference expression level is of about 100 pg/ml and the CXCR7 reference expression level is of about 250 ng/ml (plasmatic levels – ELISA assay).
In this case, a CXCL5 expression level identical to or below 100 pg/ml together with a CXCL7 expression level identical to or below 250 ng/ml is indicative of a resistance of the subject to sunitinib, and a CXCL5 expression level above 100 pg/ml together with a CXCL7 level above 250 ng/ml is indicative of a sensitivity of the subject to sunitinib.
Inventors highlighted CXCL5, CXCL7 and a combination thereof as predictive markers of sunitinib efficacy. They established a threshold value for patients for low or high risk of relapse and death in independent prospective cohort and in a retrospective cohort.
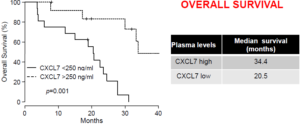
Recent results have shown an interesting validation level of CXCL7 as predictive marker of sunitinib efficacy.
BENEFITS
Identifying patients likely to respond to treatment represents a therapeutic challenge to limit the administration of ineffective toxic products. Thus, the discovery of predictive markers of response to treatment would avoid a waste of time at diagnostic and would anticipate gains treatment. The clinician would therefore choose an alternative treatment among those available (usually administered in the second or third line treatment).
The accurate selection of the patients capable of responding to a particular chemotherapy is a solution for them to receive the most appropriate therapy as soon as possible and typically as soon as they are diagnosed.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
The technology may be applied to develop a predictive diagnostic test which allows to identify at diagnostic stage the patients likely to respond to a particular therapy of renal cell carcinoma, in particular Sunitinib.