Carbon-carbon of carbon-heteroatom bonding
Référence
00755-01
Mots-clés
Statut des brevets
Provisional patent application US60/818334 filed July 5th, 2006


Inventeurs
Marc TAILLEFER
Ning XIA
Armelle OUALI
Statut commercial
Exclusive or non-exclusive licence.
Laboratoire
Institut Charles Gerhardt “Institut de chimie moléculaire et des Maériaux », in Montpellier, France
Description
CONTEXT
The formation of C-N bond is one of the most important reactions in numerous syntheses of pharmaceuticals and agrochemical compounds as well as many commercial dye molecules. The copper catalyzed Ullmann reaction has been the most used method in industry due to the attractive price of copper compared to other noble metals as palladium, ruthenium, etc…
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The invention concerns a simple and easily available system which is efficient for a wide variety of cross-coupling reactions, said catalytic system being less expensive and less toxic than the catalytic systems known previously. The combined used of iron-and copper-based compounds, as a catalytic system, allows cross-coupling reactions between a compound carrying a leaving group and a nucleophilic compound, without it being necessary to use specific ligands or specific solvents.
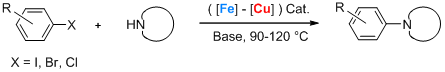
Examples: arylation, vinylation alkynylation
According to a preferred embodiment, the process of the invention uses a catalytic system comprising iron , preferably salts of iron (III)like iron (III) chloride, iron (III) acetate and iron (III) acetylacetonate together with a catalyst selected from Cu(0), CuI, CuO, Cu(acac)2 and their mixtures. The process of the invention is usually carried out in the presence of an organic solvent. It is generally conducted at temperature in the range 25°C to 140°C.
BENEFITS
– Moderate reaction temperature;
– The process of the invention involves a large number of nucleophilic compounds. The iron/copper catalytic system is less toxic and expensive than the palladium or nickel catalytic system.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
Chemical and pharmaceuticals synthesis