CNRS Innovation - De la recherche à l'innovation depuis plus de 30 ans
0
Experts à votre service
0
Contrats d'exploitation signés depuis 2012
0
Projets accompagnés en prématuration depuis 2014
0
Start-up accompagnées par RISE depuis 2019
© Jean-Claude MOSCHETTI / SPCTS / CNRS Photothèque
Notre actualité
Voir toutes les actus S’inscrire à la Lettre Innovation du CNRS La Lettre Innovation
25 avril 2024
Les levées de fonds du mois de mars 2024
Chaque mois, retrouvez les levées de fonds des entreprises issues des laboratoires sous tutelle du CNRS.
Lire la suite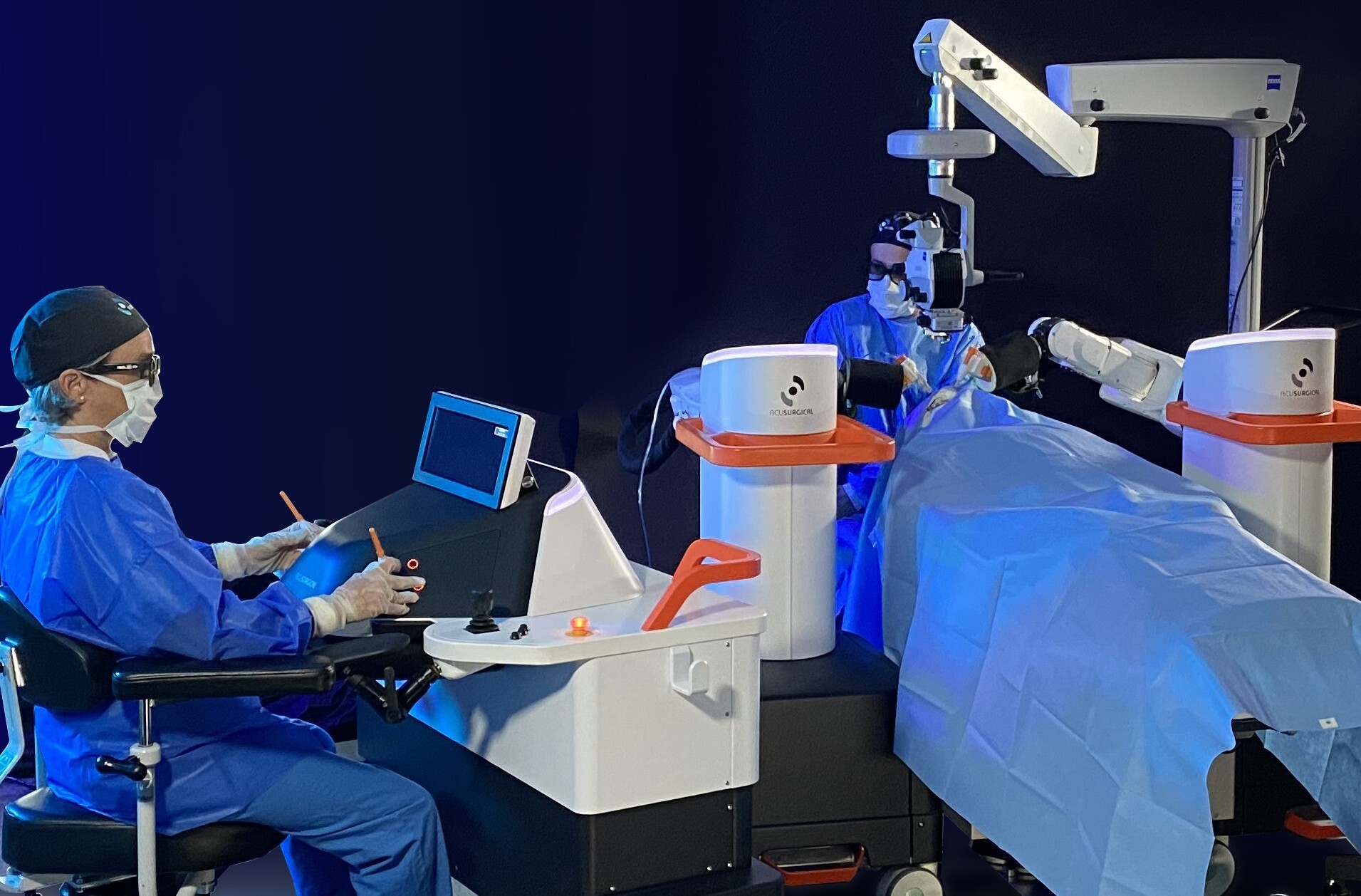
23 avril 2024
AcuSurgical : la chirurgie vitréo-rétinienne augmentée
La start-up AcuSurgical a annoncé avoir conclu – avec succès – son premier essai clinique. Sa plateforme robotisée Luca permet d’améliorer la précision et la sécurité des opérations de…
Lire la suite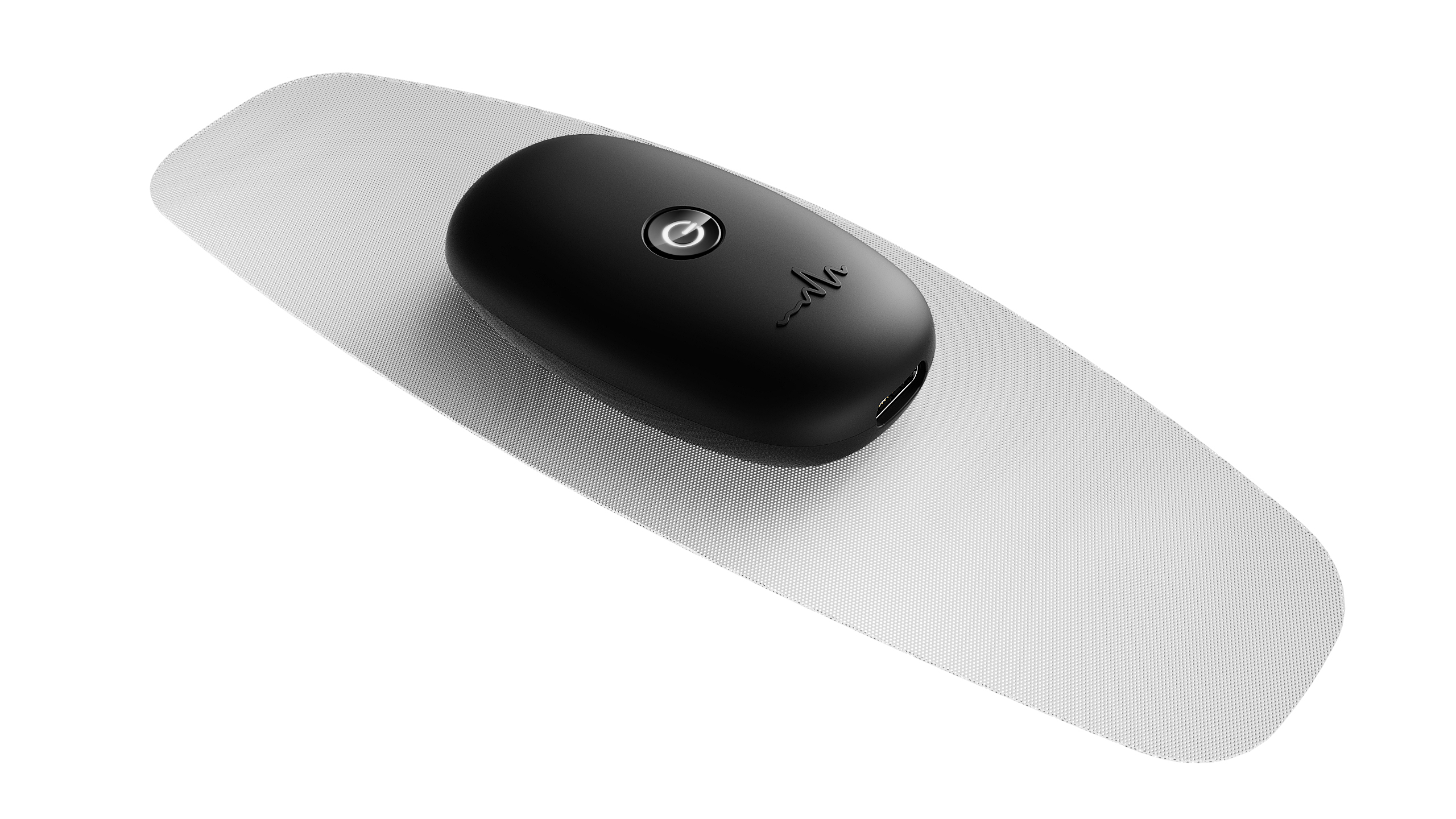
23 avril 2024
myWaves : un appareil pour améliorer nos nuits basé sur les recherches neuroscientifiques
Ce produit peut analyser les ondes delta du cerveau et créer une piste sonore améliorant la qualité du sommeil. Il est issu des travaux effectués à l’Institut des neurosciences Paris-Saclay.
Lire la suiteDonnez vie à votre projet de start-up dans les meilleures conditions
découvrez notre programme
d’accompagnement à la création de start-up
Des experts passionnés au service de l'innovation
CNRS Innovation fait converger les talents et les énergies nourries par la pluralité des profils : diplômes combinés avec expérience et savoir-faire constituent une équipe d’excellence.



