CNRS Innovation - De la recherche à l'innovation depuis plus de 30 ans
0
Experts à votre service
0
Contrats d'exploitation signés depuis 2012
0
Projets accompagnés en prématuration depuis 2014
0
Start-up accompagnées par RISE depuis 2019
© Hubert RAGUET / CEMES /CNRS Photothèque
Notre actualité
Voir toutes les actus S’inscrire à la Lettre Innovation du CNRS La Lettre Innovation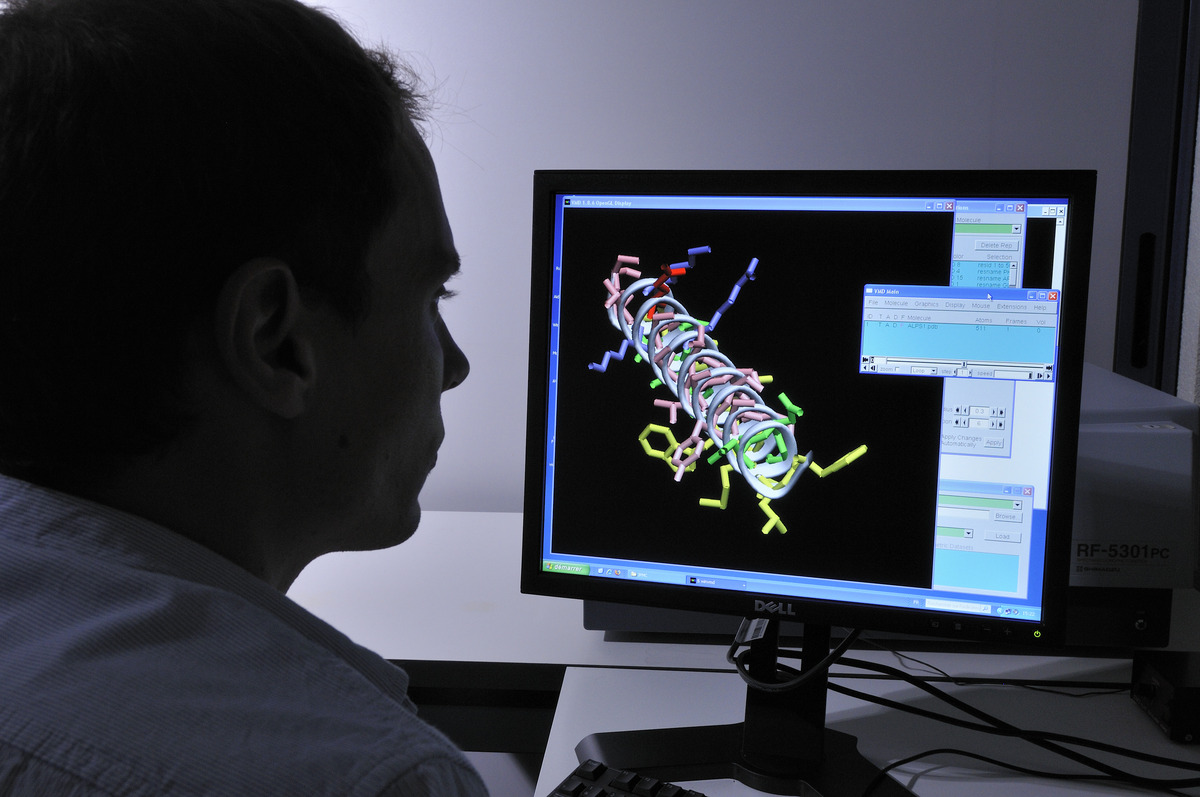
25 avril 2024
La deeptech MS4All démocratise la simulation moléculaire
MS4All, pour “Molecular Simulation for All”. Le nom de la nouvelle start-up deeptech traduit sa mission : mettre la simulation moléculaire à la disposition du plus grand nombre de…
Lire la suite
25 avril 2024
Les levées de fonds du mois de mars 2024
Chaque mois, retrouvez les levées de fonds des entreprises issues des laboratoires sous tutelle du CNRS.
Lire la suite
23 avril 2024
Cilkoa propose une alternative au plastique avec des emballages papier durables et performants
Les emballages en plastique sont un fléau écologique. C’est sur ce terrain que la start-up française Cilkoa s’est démarquée avec sa technologie conférant au papier des propriétés de…
Lire la suiteDonnez vie à votre projet de start-up dans les meilleures conditions
découvrez notre programme
d’accompagnement à la création de start-up
Des experts passionnés au service de l'innovation
CNRS Innovation fait converger les talents et les énergies nourries par la pluralité des profils : diplômes combinés avec expérience et savoir-faire constituent une équipe d’excellence.



